Default xpose box plot function
xplot_box.RdManually generate categorical covariate box plots against eta.
Usage
xplot_box(
xpdb,
mapping = NULL,
type = "b",
guide = FALSE,
yscale = "continuous",
title = NULL,
subtitle = NULL,
caption = NULL,
tag = NULL,
plot_name = "box_plot",
gg_theme,
xp_theme,
opt,
quiet,
...
)Arguments
- xpdb
An xpose database object.
- mapping
List of aesthetics mappings to be used for the xpose plot (e.g.
point_color).- type
String setting the type of plot to be used. Only 'b' applicable.
- guide
Enable guide display (e.g. unity line).
- yscale
Scale type for y axis (e.g. 'continuous', 'discrete', 'log10').
- title
Plot title. Use
NULLto remove.- subtitle
Plot subtitle. Use
NULLto remove.- caption
Page caption. Use
NULLto remove.- tag
Plot identification tag. Use
NULLto remove.- plot_name
Name to be used by
xpose::xpose_save()when saving the plot.- gg_theme
A complete ggplot2 theme object (e.g.
ggplot2::theme_classic), a function returning a complete ggplot2 theme, or a change to the currentgg_theme.- xp_theme
A complete xpose theme object (e.g.
theme_xp_default) or a list of modifications to the currentxp_theme(e.g.list(point_color = 'red', line_linetype = 'dashed')).- opt
A list of options in order to create appropriate data input for ggplot2. For more information see
data_opt.- quiet
Logical, if
FALSEmessages are printed to the console.- ...
Any additional aesthetics to be passed on
xplot_scatter.
Value
An object of class xpose_plot, ggplot, and gg. This object represents a customized plot created using ggplot2.
The xpose_plot class provides additional metadata and integration with xpose workflows, allowing for advanced
customization and compatibility with other xpose functions. Users can interact with the plot object as they
would with any ggplot2 object, including modifying aesthetics, adding layers, or saving the plot.
Faceting
Every xpose plot function has built-in faceting functionalities. Faceting arguments
are passed to the functions facet_wrap_paginate when the facets
argument is a character string (e.g. facets = c('SEX', 'MED1')) or
facet_grid_paginate when facets is a formula (e.g. facets = SEX~MED1).
All xpose plot functions accept all the arguments for the facet_wrap_paginate
and facet_grid_paginate functions e.g. dv_vs_ipred(xpdb_ex_pk,
facets = SEX~MED1, ncol = 3, nrow = 3, page = 1, margins = TRUE, labeller = 'label_both').
Faceting options can either be defined in plot functions (e.g. dv_vs_ipred(xpdb_ex_pk,
facets = 'SEX')) or assigned globally to an xpdb object via the xp_theme (e.g. xpdb
<- update_themes(xpdb_ex_pk, xp_theme = list(facets = 'SEX'))). In the latter example all plots
generate from this xpdb will automatically be stratified by `SEX`.
By default, some plot functions use a custom stratifying variable named `variable`, e.g.
eta_distrib(). When using the facets argument, `variable` needs to be added manually
e.g. facets = c('SEX', 'variable') or facets = c('SEX', 'variable'), but is optional,
when using the facets argument in xp_theme variable is automatically added whenever needed.
Layers mapping
Plots can be customized by mapping arguments to specific layers. The naming convention is layer_option where layer is one of the names defined in the list below and option is any option supported by this layer e.g. boxplot_fill = 'blue', etc.
box plot: options to
geom_boxplotyscale: options to
scale_y_continuousorscale_y_log10
Examples
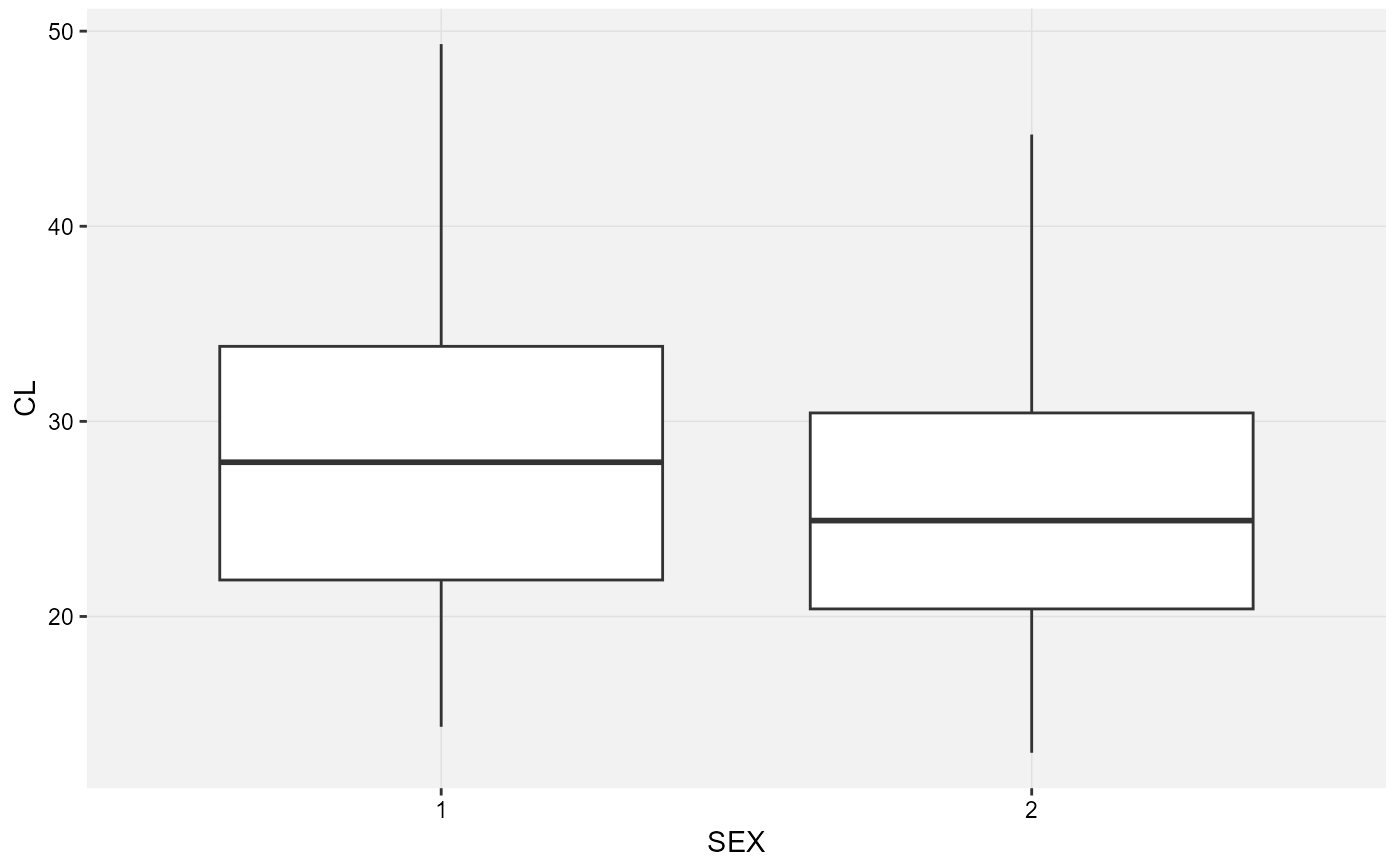
# Categorical Covariate MED1 vs ETA1
xplot_box(xpose::xpdb_ex_pk, ggplot2::aes(x = MED1, y = ETA1))
#> Using data from $prob no.1
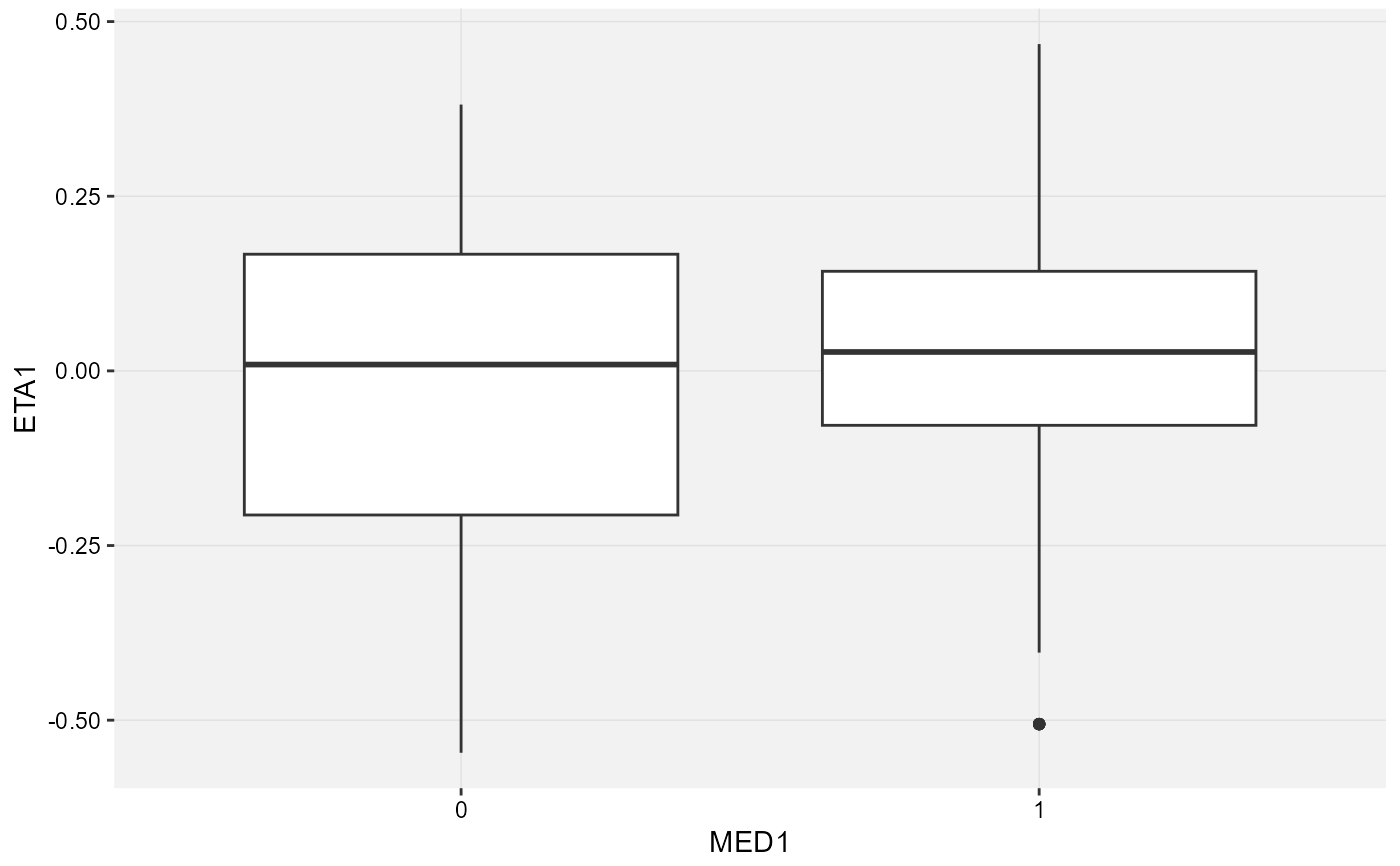 # Categorical Covariate SEX vs CL
xplot_box(xpose::xpdb_ex_pk, ggplot2::aes(x = SEX, y = CL))
#> Using data from $prob no.1
# Categorical Covariate SEX vs CL
xplot_box(xpose::xpdb_ex_pk, ggplot2::aes(x = SEX, y = CL))
#> Using data from $prob no.1